Análisis y revisión de la variación del MHC-B (complejo mayor de Histocompatibilidad) en pollos.
Síntesis del trabajo en líneas sintéticas INTA
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.19137/cienvet202224206Palabras clave:
Complejo mayor de Histocompatibilidad, pollos, Gallus gallus, MHC, aves, SNPs, haplotipos, Campero INTAResumen
El complejo mayor de Histocompatibilidad (MHC del inglés: Major histocompatibility complex) en pollos (Gallus gallus) se encuentra localizado en un micro cromosoma, el 16 del genoma aviar. Así como ocurre en otras especies tiene una fuerte asociación con la resistencia genética a enfermedades. Esta característica multigénica es particularmente deseada para la selección de esta especie, en particular por su relación con el bienestar animal. En este trabajo se pretende revisar los conocimientos sobre el análisis de la variabilidad del MHC-B en pollos y sus metodologías de análisis y una síntesis de los trabajos realizados en pollos Campero INTA
Descargas
Citas
Briles WE, McGibbon WH, Irwin MR. On multiple alleles effecting cellular antigens in the chicken. Genetics [Internet]. 1950 [cited 2018 Apr 10];35(6):633–52. Available from: http://www.genetics.org/content/genetics/35/6/633.full.pdf
Briles WE, Bumstead N, Ewert DL, Gilmour DG, Gogusev J, Hala K, et al. Nomenclature for chicken major histocompatibility (B) complex. Immunogenetics [Internet]. 1982 [cited 2018 Jun 26];15(5):441–7. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/BF00345903
Nordskog AW, Pevzner IY, Trowbridge CL, Benedict AA. Immune response and adult mortality associated with the B locus in chickens. Adv Exp Med Biol [Internet]. 1977 [cited 2018 Apr 10];88:245–56. Available from: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-1-4613-4169-7_23
Guillemot F, Kaufman JF, Skjoedt K, Auffray C. The major histocompatibility complex in the chicken. Trends Genet. 1989;5(C):300–4.
Miller MM, Goto R, Zoorob R, Auffray C, Elwood Briles W. Regions of homology shared by Rfp-Y and major histocompatibility B complex genes. Immunogenetics. 1994;39(1):71–3.
Juul-Madsen HR, Zoorob R, Auffray C, Skjødt K, Hedemand JE. Hew chicken Rfp-Y haplotypes on the basis of MHC class II RFLP and MLC analyses. Immunogenetics [Internet]. 1997 [cited 2021 Mar 5];45(6):345–52. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s002510050215
Afanassieff M, Goto RM, Ha J, Sherman MA, Zhong L, Auffray C, et al. At Least One Class I Gene in Restriction Fragment Pattern-Y ( Rfp-Y ), the Second MHC Gene Cluster in the Chicken, Is Transcribed, Polymorphic, and Shows Divergent Specialization in Antigen Binding Region . J Immunol. 2001 Mar 1;166(5):3324–33.
Kaufman J, Jacob J, Shaw J, Walker B, Milne S, Beck S, et al. Gene organisation determines evolution of function in the chicken MHC. Immunol Rev [Internet]. 1999 Feb [cited 2016 Mar 2];167(1):101–17.
Kaufman J, Milne S, Göbel TW, Walker BA, Jacob JP, Auffray C, et al. The chicken B locus is a minimal essential major histocompatibility complex. Nature [Internet]. 1999 Oct 28 [cited 2016 Mar 3];401(6756):923–5. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10553909
Chen L, Fakiola M, Staines K, Butter C, Kaufman J. Functional alleles of chicken BG genes, members of the butyrophilin gene family, in peripheral T cells. Front Immunol. 2018;9(MAY).
Página web del INTA. p. https://inta.gob.ar/documentos/prohuerta.
Livant EJ, Zheng D, Johnson LW, Shi W, Ewald SJ. Three new MHC haplotypes in broiler breeder chickens. Anim Genet. 2001;32(3):123–31.
McConnell SKJ, Dawson DA, Wardle A, Burke T. The isolation and mapping of 19 tetranucleotide microsatellite markers in the chicken. Anim Genet [Internet]. 1999 Jun [cited 2018 Jun 26];30(3):183–9. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1046/j.1365-2052.1999.00454.x
Fulton J, Juul-Madsen H, Ashwell C, McCarron A, Arthur J, O’Sullivan N, et al. Molecular genotype identification of the Gallus gallus major histocompatibility complex. Immunogenetics [Internet]. 2006;58(5):407–21. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00251-006-0119-0
Bacon LD. Influence of the major histocompatibility complex on disease resistance and productivity. Vol. 66, Poultry science. 1987. p. 802–11.
Lamont SJ. The chicken major histocompatibility complex in disease resistance and poultry breeding. J Dairy Sci [Internet]. 1989 May 1 [cited 2016 Mar 3];72(5):1328–33. Available from: http://www.journalofdairyscience.org/article/S0022030289792407/fulltext
Kaufman J, Salomonsen J. The “Minimal Essential MHC” revisited: Both peptide-binding and cell surface expression level of MHC molecules are polymorphisms selected by pathogens in chickens. Hereditas.1997;127(1–2):67–73.
Bacon LD, Witter RL. Influence of B-Haplotype on the Relative Efficacy of Marek’s Disease Vaccines of Different Serotypes. Avian Dis [Internet]. 1993 Jan [cited 2018 Apr 10];37(1):53. Available from: https://www.jstor.org/stable/1591457?origin=crossref
Wakenell PS, Miller MM, Goto RM, Gauderman WJ, Briles WE. Association between the Rfp-Y haplotype and the incidence of Marek’s disease in chickens. Immunogenetics [Internet]. 1996 Jan [cited 2016 Mar 3];44(4):242–5. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8753853
Cole RK. Studies on Genetic Resistance to Marek’s Disease. Avian Dis. 1968 Feb;12(1):9.
Ewald SJ, Livant EJ. Distinctive polymorphism of chicken B-FI (major histocompatibility complex class I) molecules. Poult Sci [Internet]. 2004 Apr [cited 2016 Mar 2];83(4):600–5. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15109057
Livant EJ, Ewald SJ. High-resolution typing for chicken BF2 (MHC class I) alleles by automated sequencing. Anim Genet. 2005 Oct;36(5):432–4.
Hepkema BG, Hensen EJ, Blankert JJ, Zijpp AJ, Albers GAA, Tilanus MGJ, et al. Mapping of susceptibility to Marek’s disease within the major histocompatibility (B) complex by refined typing of White Leghorn chickens. Anim Genet [Internet]. 2009 Apr 24 [cited 2021 Mar 5];24(4):283–7. Available from: http://doi.wiley.com/10.1111/j.1365-2052.1993.tb00312.x
Juul-Madsen HR, Dalgaard TS, Guldbrandtsen B, Salomonsen J. A polymorphic major histocompatibility complex class II-like locus maps outside of both the chicken B-system and Rfp-Y-system. Eur J Immunogenet [Internet]. 2000 Apr [cited 2016 Mar 2];27(2):63–71. Available from: http://www.readcube.com/articles/10.1046%2Fj.1365-2370.2000.00200.x?r3_referer=wol&tracking_action=preview_click&show_checkout=1&purchase_referrer=onlinelibrary.wiley.com&purchase_site_license=LICENSE_DENIED
Iglesias GM, Soria LA, Goto RM, Jar AM, Miquel MC, Lopez OJ, et al. Genotypic variability at the major histocompatibility complex (B and Rfp-Y) in Camperos broiler chickens. Anim Genet. 2003;34(2).
Goto RM, Afanassieff M, Ha J, Iglesias GM, Ewald SJ, Briles WE, et al. Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) assays for major histocompatibility complex B genotyping in chickens. Poult Sci. 2002;81:1832–41.
Fulton JE, McCarron AM, Lund AR, Pinegar KN, Wolc A, Chazara O, et al. A high-density SNP panel reveals extensive diversity, frequent recombination and multiple recombination hotspots within the chicken major histocompatibility complex B region between BG2 and CD1A1. Genet Sel Evol [Internet]. 2016;48(1):1. Available from: http://www.gsejournal.org/content/48/1/1
Lima-Rosa CA V, Canal CW, Streck AF, Freitas LB, Delgado-Cañedo A, Bonatto SL, et al. B-F DNA sequence variability in Brazilian (blue-egg Caipira) chickens. Anim Genet. 2004;35(4):278–84.
Goto R, Miyada CG, Young S, Wallace RB, Abplanalp H, Bloom SE, et al. Isolation of a cDNA clone from the B-G subregion of the chicken histocompatibility (B) complex. Immunogenetics [Internet]. 1988 Jan [cited 2016 Mar 3];27(2):102–9. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2826332
Uni Z, Sklan D, Haklay N, Yonash N, Heller D. Response of three class-IV major histocompatability complex haplotypes to Eimeria acervulina in meat-type chickens. Br Poult Sci. 1995 Sep 1;36(4):555–61.
Iglesias GM, Huguet MJ, Goto RM, Miquel MC, Miller MM. Report of new alleles at BG loci in Camperos chickens. BAG - J Basic Appl Genet [Internet]. 2007 [cited 2016 Mar 2];18(1):29–30. Available from: http://www.scielo.org.ar/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1852-62332007000100006&lng=es&nrm=iso&tlng=en
Worley K, Gillingham M, Jensen P, Kennedy LJ, Pizzari T, Kaufman J, et al. Single locus typing of MHC class I and class II B loci in a population of red jungle fowl. Immunogenetics. 2008;60(5):233–47.
Chazara O, Chang C, Bruneau N. Diversity and evolution of the highly polymorphic tandem repeat LEI0258 in the chicken MHC - B region. 2013;447–59.
Nguyen-phuc H, Fulton JE, Berres ME. Genetic variation of major histocompatibility complex ( MHC ) in wild Red Junglefowl ( Gallus gallus ). 2012;400–11.
Han B, Lian L, Qu L, Zheng J, Yang N. Abundant polymorphisms at the microsatellite locus LEI0258 in indigenous chickens. Poult Sci [Internet]. 2013 Dec 1 [cited 2016 Mar 3];92(12):3113–9. Available from: http://ps.oxfordjournals.org/content/92/12/3113.full
Nikbakht G, Esmailnejad A, Barjesteh N. LEI0258 microsatellite variability in Khorasan, Marandi, and Arian chickens. Biochem Genet. 2013 Jun;51(5–6):341–9.
Manjula P, Park HB, Seo D, Choi N, Jin S, Ahn SJ, et al. Estimation of heritability and genetic correlation of body weight gain and growth curve parameters in Korean native chicken. Asian-Australasian J Anim Sci. 2018 Jan 1;31(1):26–31.
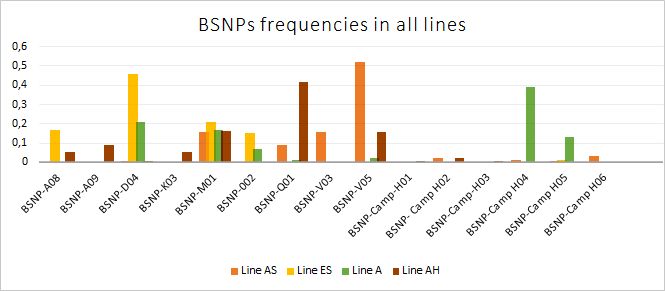
Iglesias GM, Canet ZE, Cantaro H, Miquel MC, Melo JE, Miller MM, et al. Mhc-B haplotypes in “Campero-Inta” chicken synthetic line. Poult Sci. 2019 Nov 1;98(11):5281–6.
Iglesias GM, Beker MP, Remolins JS, Canet ZE, Librera J, Cantaro H, et al. MHC-B variation in maternal and paternal synthetic lines of the Argentinian Campero INTA chicken. Poult Sci. 2021 Aug 1;100(8):101253.
Chazara O, Minvielle F, Roux D, Bed’hom B, Feve K, Coville JL, et al. Evidence for introgressive hybridization of wild common quail (Coturnix coturnix) by domesticated Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica) in France. Conserv Genet. 2010;11(3):1051–62.
Nguyen-Phuc H, Fulton JE, Berres ME. Genetic variation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) in wild Red Junglefowl (Gallus gallus). Poult Sci. 2016 Feb 25;95(2):400–11.
Fulton JE, Berres ME, Kantanen J, Honkatukia M. MHC-B variability within the Finnish Landrace chicken conservation program. Poult Sci. 2017;96(9):3026–30.
Tarrant KJ, Lopez R, Loper M, Fulton JE. Assessing MHC-B diversity in Silkie chickens. Poult Sci. 2020 May 1;99(5):2337–41.
Wang H, Ma T, Chang G, Wan F, Liu X, Liu L, et al. Molecular Genotype Identification of Different Chickens: Major Histocompatibility Complex. Open Access J Sci Technol [Internet]. 2014 Sep 27 [cited 2016 Mar 3];2:1–7. Available from: http://www.agialpress.com/journals/oajost/2014/101111/
Lwelamira J, Kifaro GC, Gwakisa PS, Msoffe PLM. Association of LEI0258 microsatellite alleles with antibody response against newcastle disease virus vaccine and body weight in two Tanzania chicken ecotypes. African J Biotechnol. 2008;7(6):714–20.
Hunt HD, Jadhao S, Swayne DE. Major histocompatibility complex and background genes in chickens influence susceptibility to high pathogenicity avian influenza virus. In: Avian Diseases [Internet]. Avian Dis; 2010 [cited 2020 Aug 18]. p. 572–5. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20521696/
Boonyanuwat K, Thummabutra S, Sookmanee N, Vatchavalkhu V, Siripholvat V. Influences of major histocompatibility complex class I haplotypes on avian influenza virus disease traits in Thai indigenous chickens. Anim Sci J. 2006;77(3):285–9.
Miller MM, Taylor RL. Brief review of the chicken Major Histocompatibility Complex: The genes, their distribution on chromosome 16, and their contributions to disease resistance. Poult Sci. 2016 Feb 25;95(2):375–92.
Dunnington EA, Briles WE, Briles RW, Siegel PB. Immunoresponsiveness in Chickens: Association of Antibody Production and the B System of the Major Histocompatibility Complex. Poult Sci. 1996;75(10):1156–60.
Gao Liu GF, Liu J, Zhou X, Kaufman J, Xia C, Zhang J, et al. Disease Susceptibility of B4 Chickens Peptide Transporter Restriction Can Explain MHC Class I Molecule BF2*0401 Plus Narrow Groove and Restricted Anchors of. J Immunol Ref [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Jul 1];189:4478–87. Available from: http://www.jimmunol.org/content/189/9/4478http://www.jimmunol.org/content/189/9/4478.full#ref-list-1
Livant EJ, Ewald SJ. High-resolution typing for chicken BF2 (MHC class I) alleles by automated sequencing. Anim Genet. 2005;36(5):432–4.
Ewald SJ, Ye X, Avendano S, McLeod S, Lamont SJ, Dekkers JCM. Associations of BF2 alleles with antibody titres and production traits in commercial pure line broiler chickens. Anim Genet. 2007 Apr;38(2):174–6.
Haunshi S, Devara D, Ramasamy K, Ullengala R, Chatterjee RN. Genetic diversity at major histocompatibility complex and its effect on production and immune traits in indigenous chicken breeds of India. Arch Anim Breed. 2020;63:173–82.
Genious 5.6 [Internet]. Available from: http://www.geneious.com/
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Al momento de enviar sus contribuciones, los colaboradores deberán declarar , de manera fehaciente, que poseen el permiso del archivo o repositorio donde se obtuvieron los documentos que se anexan al trabajo, cualquiera sea su formato (manuscritos inéditos, imágenes, archivos audiovisuales, etc.), permiso que los autoriza a publicarlos y reproducirlos, liberando a la revista y sus editores de toda responsabilidad o reclamo de terceros , los autores deben adherir a la licencia Creative Commons denominada “Atribución - No Comercial CC BY-NC-SA”, mediante la cual el autor permite copiar, reproducir, distribuir, comunicar públicamente la obra y generar obras derivadas, siempre y cuando se cite y reconozca al autor original. No se permite, sin embargo, utilizar la obra con fines comerciales.





4.png)


7.png)






